Hyaline Cartilage Definition
In the human body, hyaline cartilage is found in areas such as the nose, ears, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is a glossy, greyish-white tissue with a uniform appearance, and the word hyaline means “glass-like”. In addition to elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage, it is one of three types of cartilage. In the body, hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type.
Function of Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is high in collagen, a protein also found in connective tissue, skin, and bones that helps hold the body together. In different parts of the body, hyaline cartilage provides support and flexibility. The trachea and larynx, as well as sections of the respiratory system such as the nose and ears, contain this substance, which helps give these parts their shape while allowing them to move.
As hyaline cartilage covers the articular surfaces of bones (the surfaces of joints), it is called articular cartilage. When bones meet at joints, articulating cartilage acts as a shock absorber and reduces friction. The cartilage can wear away as a person ages, causing joint pain and swelling that sometimes requires surgery to alleviate.
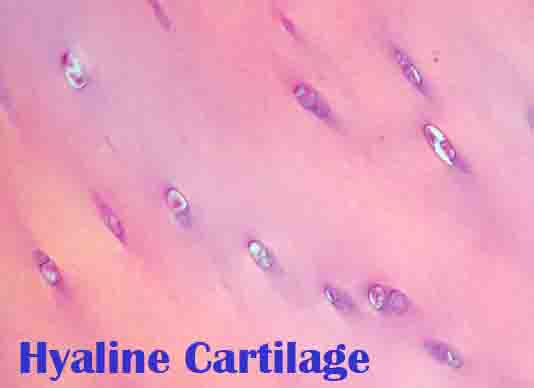
Structure of Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage contains a large amount of collagen; in particular, type II collagen. Almost all of the collagen in the human body is type I, which is found in bones, organs, skin, and tendons. Cartilage, however, consists of type II collagen.
The molecule chondroitin sulfate is also present in hyaline cartilage, which helps it resist compression. Due to its fine collagen fibers, it is the weakest of the three types of cartilage.
There are no nerves or blood vessels in cartilage tissue. The cartilage has a simple structure consisting of chondrocytes embedded in an intracellular matrix. Cells have one or two nuclei and clear protoplasm (inside content).
Chondrocytes are found in lacunae, which are small cavities surrounding them. One chondrocyte is contained in a primary lacuna. The daughter cells of that cell divide to form new boundary layers called secondary lacunae, and the group of cells with lacunae is called a cell nest.
There is a very uniform appearance to hyaline cartilage. Since cartilage tissue lacks blood vessels, it is surrounded by a membrane called the perichondrium, which provides nutrients.
Other Types of Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
The outer ear, the Eustachian tube (auditory tube), and the epiglottis, which separates the trachea and esophagus, are all lined with elastic cartilage, also called yellow cartilage. In addition to having yellow elastic fibers, it is very flexible like hyaline cartilage. These areas receive shape and support from it.
Fibrocartilage
In the pubic symphysis, between vertebrae in the spine, and in the temporomandibular joint (jaw), fibrocartilage is found. It consists of cartilage tissue and white fibrous tissue. It is also the only type of cartilage that contains both type I and type II collagen. The material has a high degree of flexibility, toughness, and elasticity.
Related Biology Terms
- An example of cartilage is the nose, ear, joints, and respiratory system, where it is a tough yet flexible connective tissue.
- Human skin and connective tissue contain collagen, the most common protein in the body.
- An elongated filament found in connective tissue is called a fiber (anatomy).
- The perichondrium is a layer of connective tissue that surrounds hyaline cartilage and elastic cartilage that plays an important role in growth, repair, and nutrient transport.